Network Reconnaissance Tools
SpiderFoot Tutorial
NOTICE: All the tutorials on this website are meant to help you find security vulnerabilties on your own network and devices to understand your security posture before black hats do. Penetration testing without a written consent is illegal and you can be prosecuted. Use these tutorials to secure your own networks or those whose permission you have been granted. Keep it ethical and keep it professional.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to SpiderFoot
- Install SpiderFoot
- Using SpiderFoot
- Scanning using SpiderFoot
- Viewing SpiderFoot scan results
Introduction to spiderfoot
SpiderFoot is an open-source OSINT automation tool that automates the process of collecting information from various public sources, including social media, DNS, WHOIS, and more.Runs on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
In my opinion, it is one of the best OSINT tools you can have in your arsenal as a penetration tester or ethical hacker
installation of spiderfoot
For Kali Linux, the tool come pre-installed, if not you can run the following command or the equivalent for your distribution
sudo apt install spiderfoot
You can also get the github repository
spiderfoot usage
To begin using the tool, you first need to setup the webserver. This can be done easily using the following command
spiderfoot 127.0.0.1:5000
You can use your own port number other than 5000.

Once the web server is started, you can navigate to the address on your web browser. I opened firefox and opened the link "127.0.0.1:5000"

Once opened you can see that you are able to run a scan, there are presets for different types of scans but first insert the name of the scan and the target. In this screenshot I targeted cyberacademy.ac.zm and the name of the scan was cyber.
On the type of scan, I went with the first option that scans for everything. It is not covert and can alert an Intrusion Detection System. But there are other options like footprint, passive and investigate each with their own parameters.

You can also go to the next tab "By Required Data" and see that you can pick specific things to look for. Check through the tab and see that there are many options to select.

There are also options to use specific modules or APIs on the third tab "By Module". I just went with the first with the usecase and selected the "everything option".

You can then go to the "scans" page to see your scan running or if is completed. We can begin seeing the results even before the scan is completed. Simply click on the scan name and you be be dropped to the summary page.
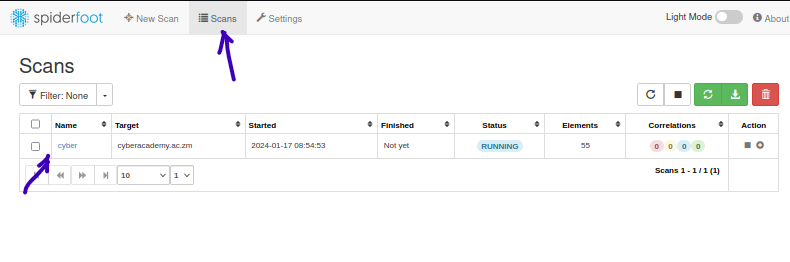
From the summary, you can see an overview but I prefer the browse section as it is more detailed on the different things it finds. Click on the browse tab.

You can see the different information that has been found categorised well.

You can scroll down to see all of what it gathers as it completes the recon. You can click on any item to see the values found such as the email addresses, domain names, http status codes, security headers and so on.